How To Take Input In Java Program
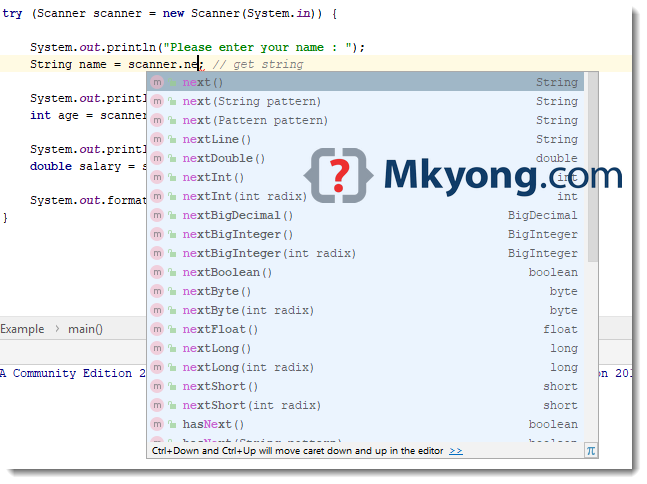
1 nextint to input an integer.
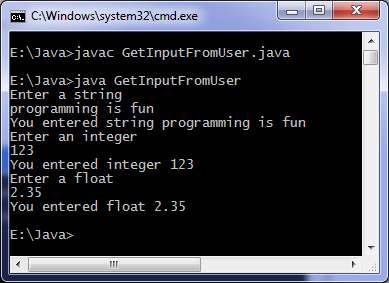
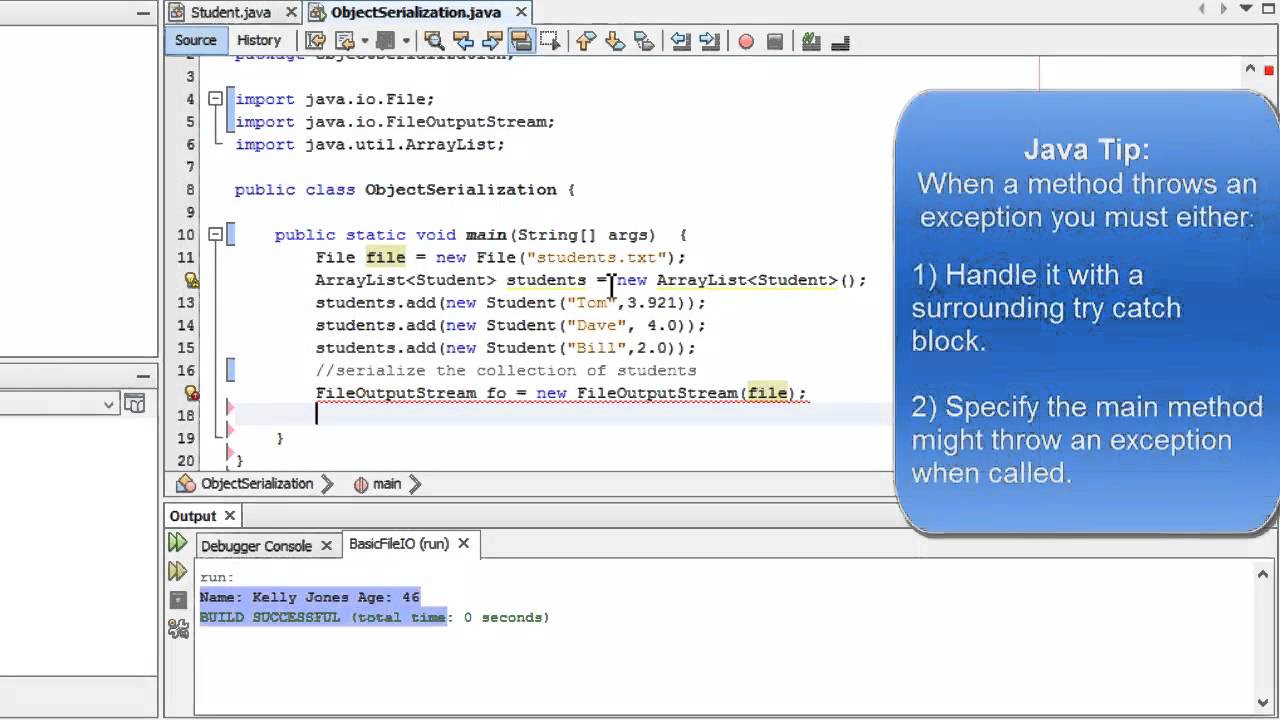
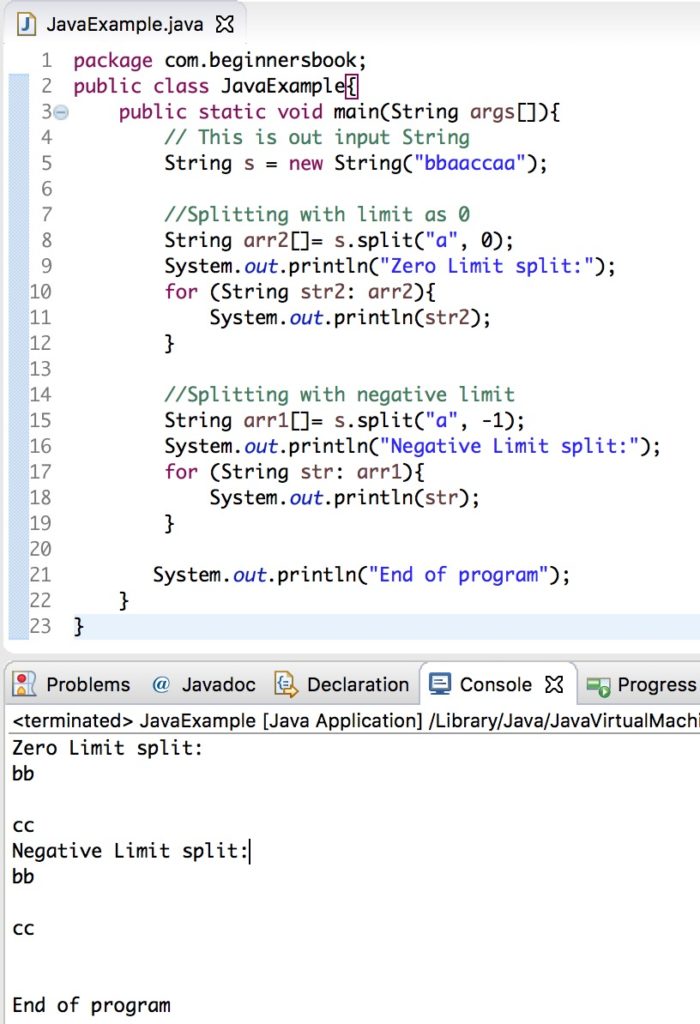
How to take input in java program. To use the scanner class create an object of the class and use any of the available methods found in the scanner class documentation. Create an object of scanner scanner input new scanner system in. Here x is the name of the object the new keyword is used to allocate memory and system in is the input stream. How to get input from user in java java scanner class.
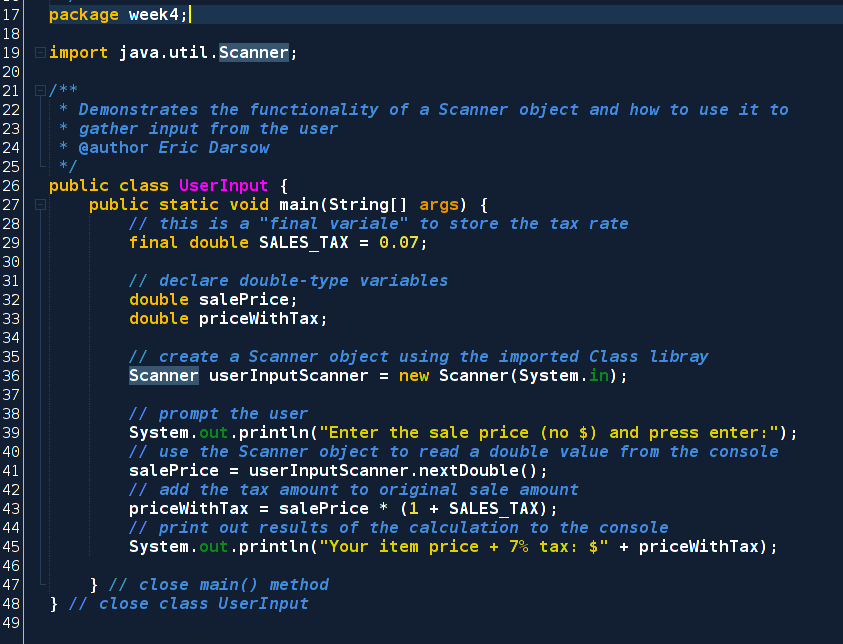
It is the easiest way to read input in java program. Scanner x new scanner system in. The nextline method of scanner class is used to take a string from the user. It belongs to java util package.
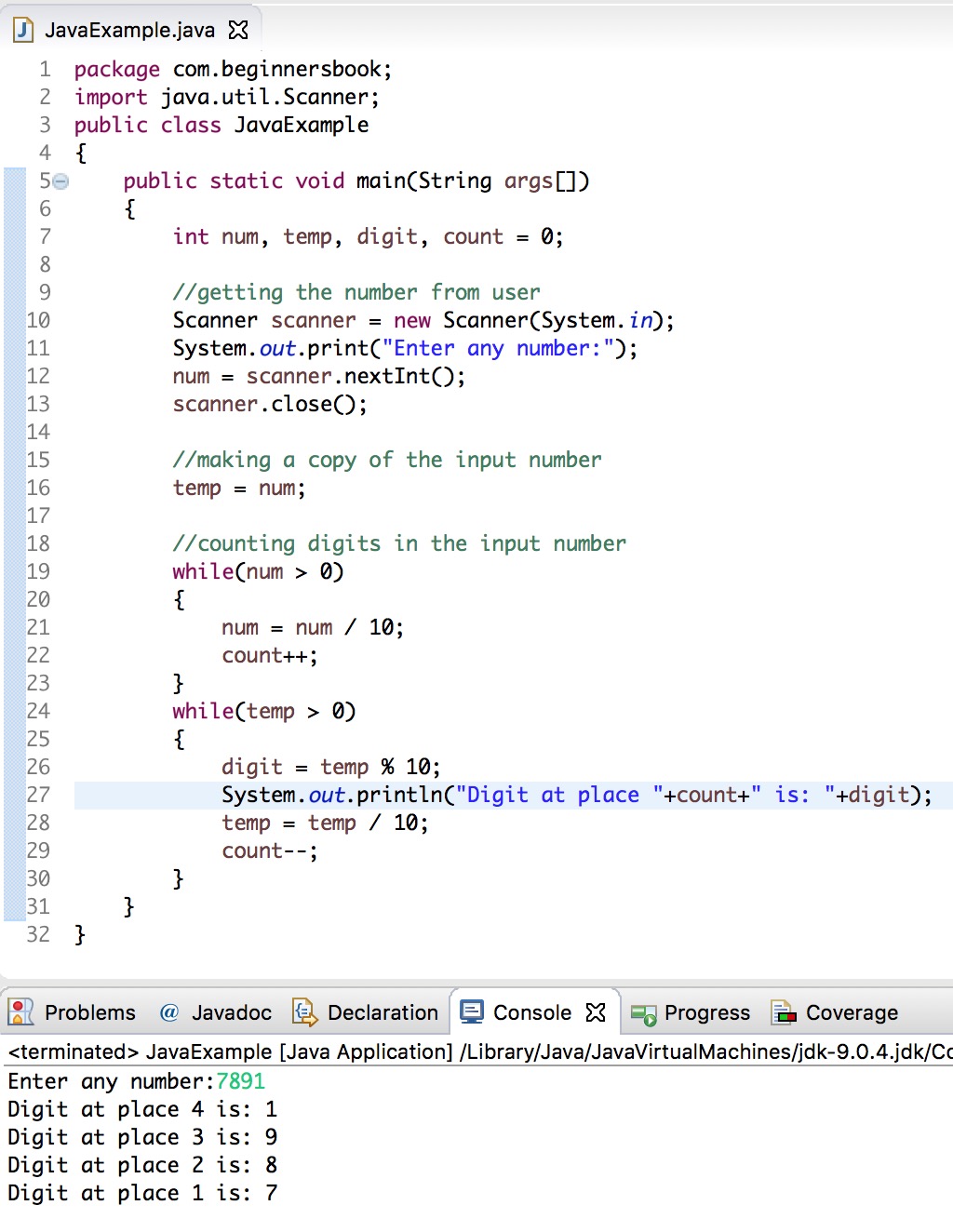
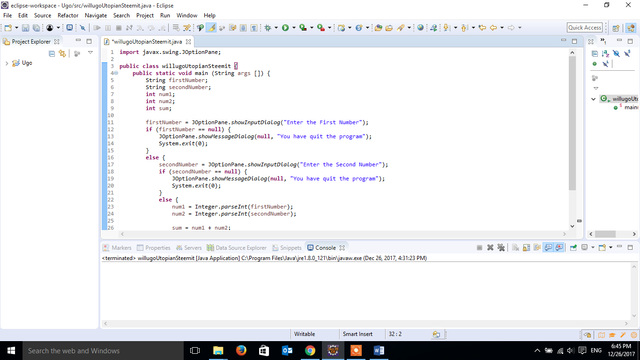
First we will develop a program to get array input from the end user through the keyboard and later we will develop a java program to take an array as argument. It is defined in java util scanner class. Prerequisite array in java java program to get array input from end user. Our program uses the following three methods.
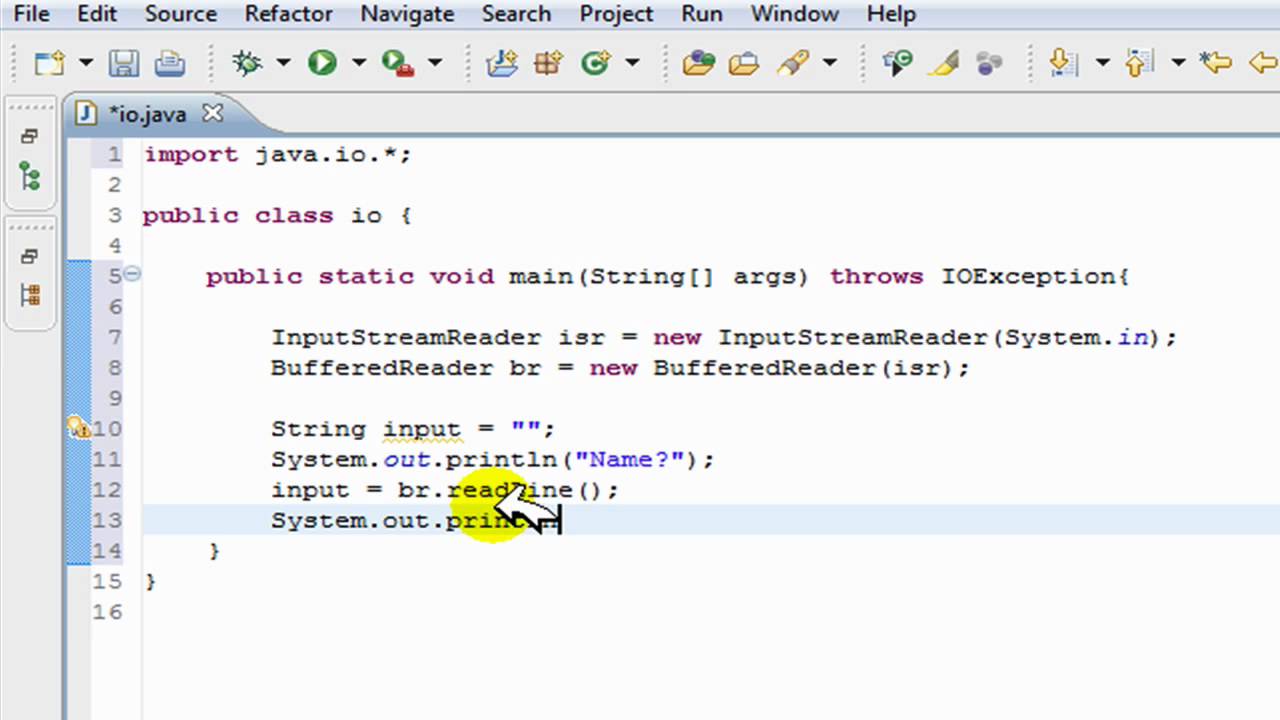
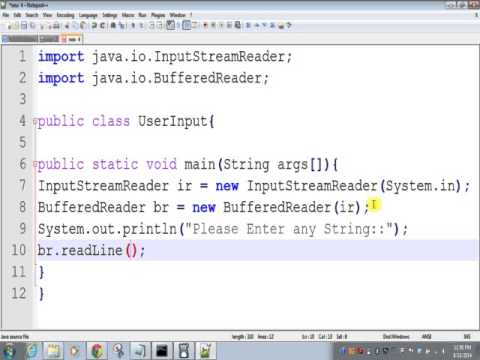
This is the java classical method to take input introduced in jdk1 0. Bufferedreader and inputstreamreader class. To learn more about importing packages in java visit java import packages. Then we need to create an object of the scanner class.
3 nextline to input a string. Take input from the user int number input nextint. After reading the line it throws the cursor to the next line. This method is used by wrapping the system in standard input stream in an inputstreamreader which is wrapped in a bufferedreader we can read input from the user in the command line.
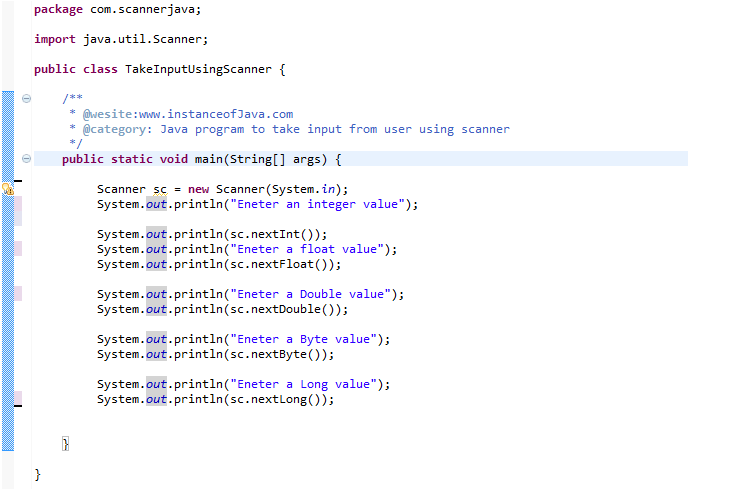
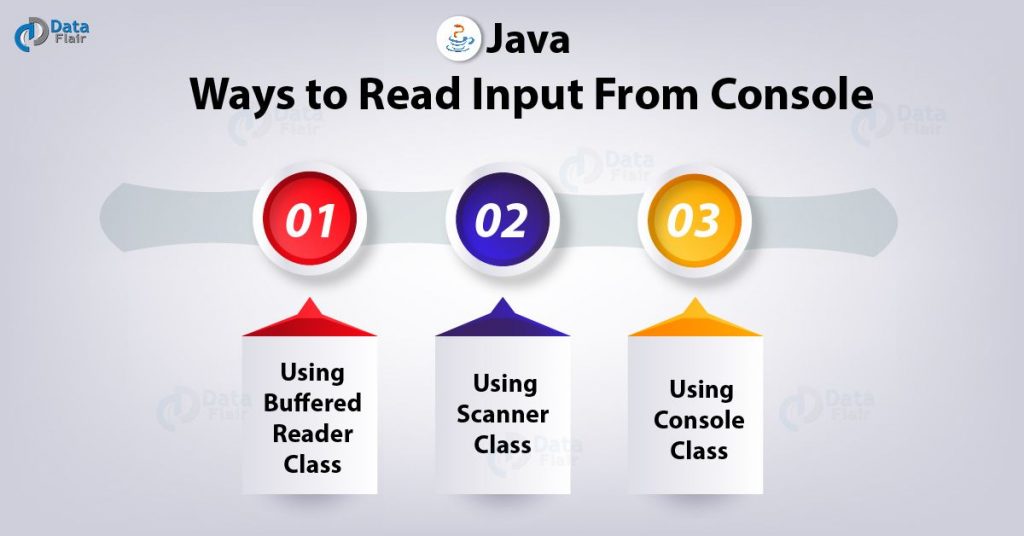
There are mainly five different ways to take input from user in java using keyboard. The scanner class is used to get user input and it is found in the java util package. We can get array input in java from the end user or from a method. Java scanner class allows the user to take input from the console.
In our example we will use the nextline method which is used to read strings. We can use the object to take input from the user. It is used to read the input of primitive types like int double long short float and byte.