How To Take Pulse In Ankle
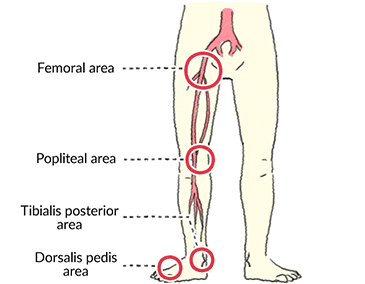
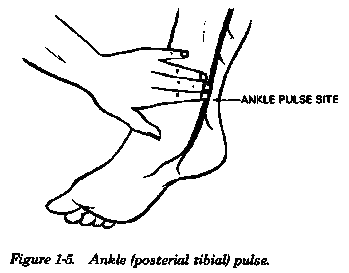
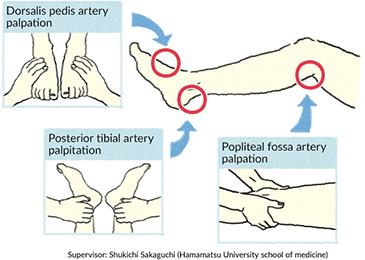
For example pulse you find in your ankle is the posterior tibial pulse while the pulse behind your knee is the popliteal pulse.
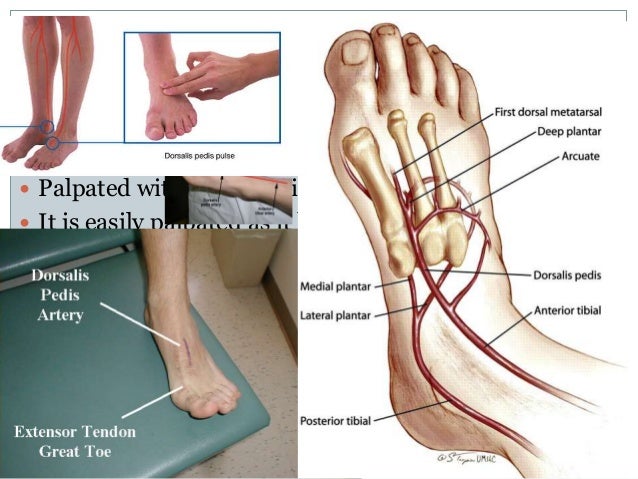
How to take pulse in ankle. The technician will start by putting a. Rest your fingers on the bony area located between the first two toes of the foot to locate the pulse. The pulse in the foot can be felt in either the dorsalis pedis or the tibialis posterior arteries according to patient plus. Slide your fingers downward approximately halfway down the top of the foot.
Listen to the pulse. Finding these pulses is simply a matter of knowing where to feel you need to position your fingers in a particular way to detect these pulses see references 1. Two possible positions to check. Place two fingers at crease of the ankle directly above the area between the big toe and the second toe.
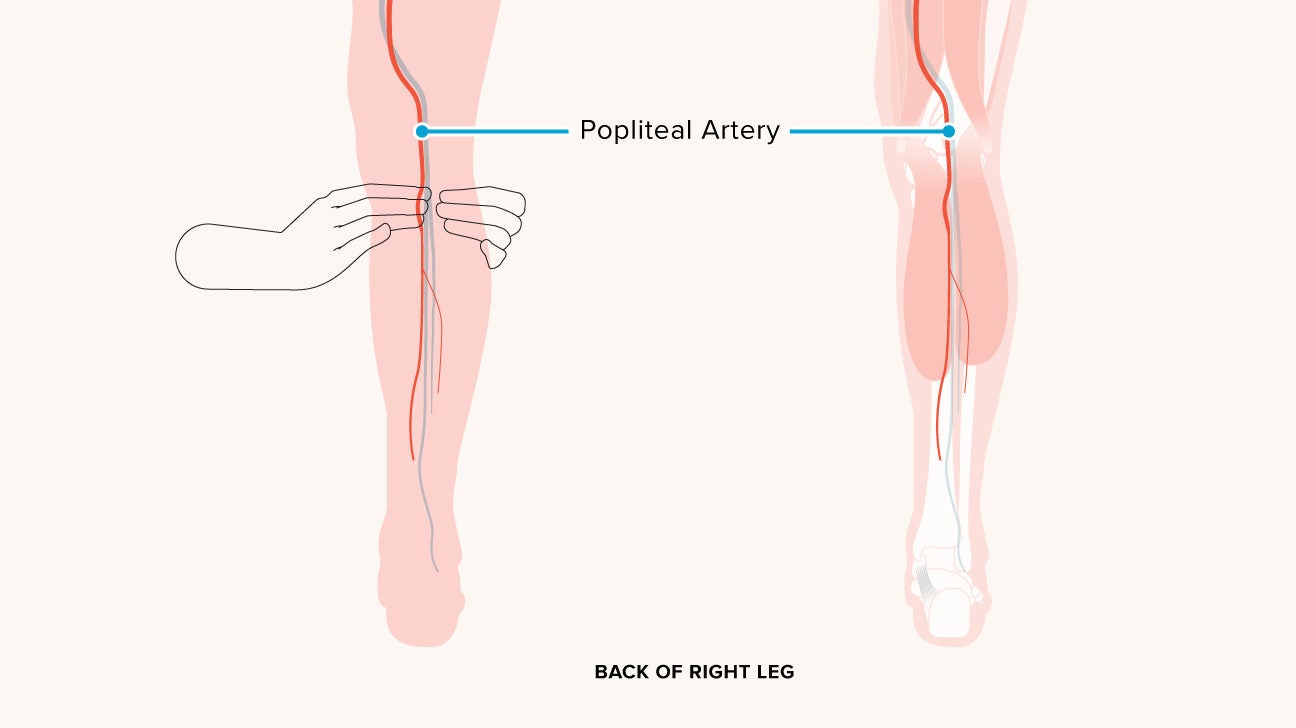
Check for either the dorsalis pedis pulse on the top of the foot or the posterior. For dorsalis pedis first. Deflate the cuff and take note when the whooshing sound returns. Often the popliteal pulse is obscured by the gastrocnemius muscle.
How do you take the pulse of the foot. Record the blood pressure of the dp artery. The popliteal pulse can be felt behind the knee toward the lateral aspect of the popliteal fossa. Squeeze the bulb to inflate the cuff.
Visualize skin for pulsation. This means that it is not uncommon to need to press deeply between the gastrocnemius muscle heads to feel the pulse. Open the blood pressure valve slowly so that pressure falls at a rate of about 2 mm hg per second. Inflate the blood pressure cuff to about 20 mmhg above the patient s regular systolic pressure or until the whooshing sound from the doppler is gone.
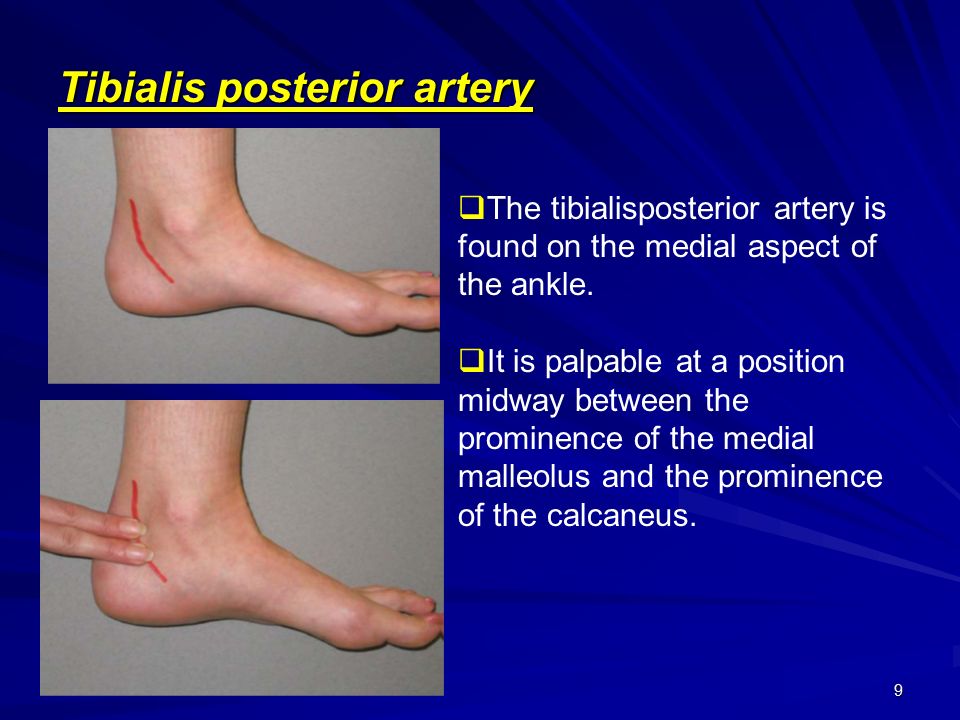
The foot pulses are felt in the same fashion as feeling any pulse namely by lightly pressing the tip of the fingers against the artery explains patient plus. The university of sydney shows that the dorsalis pedis runs along the top of the foot and the tibialis posterior artery runs just behind the ankle bone. Using this technology we can better assess the blood flow to the area dr. This is the systolic blood pressure of the ankle.
A technician will take your blood pressure in both arms and in both ankles using an inflatable cuff and a handheld ultrasound device to hear your pulse. Reposition to normal. Continue squeezing until the gauge reads 30 mm of mercury hg above the point at which the pulse could no longer be heard.